A few weeks ago while my daughter and I were shopping, we met another mom with her daughter. As happens frequently with littles, we stopped to chat and play amidst the racks. As the mom and I watched the girls navigate each other, we did our own exploring. She asked me if my daughter (who was clearly older than hers) went to preschool, and I said she did a few days a week. I returned the question, and she told me her plans for her daughter along with some other family details. It turns out she came here with her husband and young child and left their friends and families behind in India. She was eager to have an open mind to speak to, and I quickly became her consult on preschools in Austin.
After a few minutes covering preschool options in the area, she mentioned elementary school. She said something like, “I mean, I want my daughter to get a really good education.”
I heard her, acknowledged it, and responded, “Yes! I think most, if not all, parents would say that they want their children to get a really good education.” The thing is, I continued, what each person means by that is probably very different. For example, I continued, I would imagine that your idea of a really good education is probably distinctly different from mine.
I walked right into it, although I didn’t see it coming. She said, “Okay, so tell me, what is your idea of a really good education?”
“How much time do you have?” I immediately joked back, thinking there was no way I was going to be able to summarize my answer, nor did I want to try. Somehow, my humor was lost in translation, as she was clearly awaiting my response. So I took a deep breath and was surprised at how easy it was for me to tell her. I wish I had been recording myself; what I said went something like this:
1. Safe and Open Environment
To me, a really good education is about having an environment that is safe in all ways—physically, emotionally, psychically. Where the teachers are the guides, not the know-it-alls, the ones holding the space, grounded in a set of shared intentions for an experience, not a specific outcome. A place where it is safe for each child and each person to be exactly who they are, and are honored for their place and presence in the community. A place where each child is treated with kindness, patience, and appreciation and is truly seen. In order for this to happen, I understand that it will take teachers, mentors, leaders, and guides who are aware, conscious, and present.
2. All Senses Ignited
A really good education means a place where the children’s senses (all six of them) are ignited. Not at the same time, of course, and not to a point of overstimulation, but in an organic balance of sensory exploration. School is a place where who my child is, what she is passionate about, what makes her come alive, should be explored every day and in many ways. Cooking and eating, singing and dancing, creating meaningful movement, art of every sort, a lot of appropriate touch, and an honoring of each child’s unique knowing (intuition) and fantasy creations are integral and imperative.
3. Autonomy and Independence
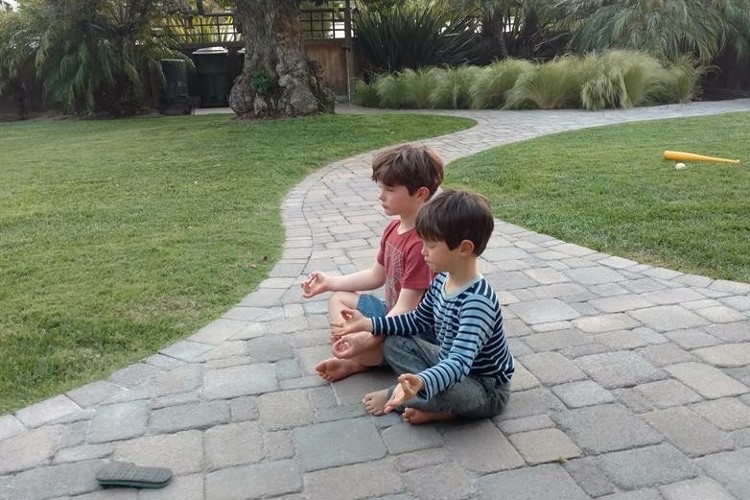
A really good education fosters autonomy and independence in every child at their unique comfort and developmental level. I visited a private alternative school in Florida earlier in the year where they call any exams given to the students “celebrations” because they see them as an opportunity for the students to celebrate what they have learned. They teach the children how to prepare their brains and their bodies for the celebrations, knowing that they can be a heightened experience. They begin in preschool teaching about the brain, how to notice what part of their brains they are in, and then exploring meditation and mindfulness techniques with the students to help bring awareness and centering. It was powerful to see that in practice.
That is just one example of what I mean when I say autonomy and independence. A really good education means our children will learn skills that will equip them in being in the world in a meaningful and powerful way. I want to see our children develop an understanding of currency early on and learn how to create a relationship to it that will serve them their whole lives. I want our children to understand that while we are each unique learners, we are a part of one world community, and while we need to foster self-reliance, we must also accept and invite the support of everything and everyone around us. I want our children to learn to advocate for who they are and for what they believe with their strong, capable voices.
4. Learning to Love
Within a really good educational system, children come to learn about what they love and even more than that, develop a love of self. Shouldn’t part of a formal education be about learning to have a relationship with yourself? What I know is that having a relationship with anyone else depends first on how I learn to treat, love, and respect myself. So we do a disservice to our children when we put so much emphasis on their learning how to navigate relationships outside of themselves without at the very least acknowledging and appreciating the connection to the most important relationship we will ever have, the one with ourselves. Yes, learning compassion and empathy is integral, but that love must also include ourselves.
What would our world look like if this were emphasized not just in our homes but also in our schools? A learning of what each child loves, a learning of what it means to love, a learning of how to love, both self and others, and lots and lots of space to practice over and over again—that is education at its highest.
5. Nature Education
I am a full believer that if there is something valuable to learn, about 99 percent of the time nature can teach it to us. It is therefore vital for our children to spend time outside and in nature. Outdoor classrooms, plenty of time in the sun, rain, dirt, and mud, exploring, creating, absorbing, and just being. Learning how to plant seeds and watch them grow. Learning how plants can heal. Learning how to care for, connect to, and treat animals. Learning how to protect our planet. These are just a few examples of all the natural world has to offer, teach, and share with us.
6. Inspired Learning
How we learn something is more important than what we are learning. It is the difference between absorption of knowledge and regurgitation of facts or figures. A really good education means that the way my child is taught to read, to do math, and to write is evolved, is itself a transformative experience.
The environment itself speaks to the learning potential. I don’t want my child to learn in the ways I learned, not because it wasn't effective for me but because we have a whole new set of tools to use. A really good education means current, innovative programs, models, and systems that are being created in present time. It also means that learning is inspired by intrinsic interest, passion, and joy and not based on external rewards, test scores, or societal norms and expectations. We are born wired to learn. When we set up an environment for children where learning becomes something to do (with incentives, competitiveness, and pressure) instead of something to be (with expansiveness, willingness, and curiosity), it changes the spirit in which we come to know ourselves and our world.